5 Geometry operations
E1. Generate and plot simplified versions of the nz dataset.
Experiment with different values of keep (ranging from 0.5 to 0.00005) for ms_simplify() and dTolerance (from 100 to 100,000) st_simplify().
- At what value does the form of the result start to break down for each method, making New Zealand unrecognizable?
- Advanced: What is different about the geometry type of the results from
st_simplify()compared with the geometry type ofms_simplify()? What problems does this create and how can this be resolved?
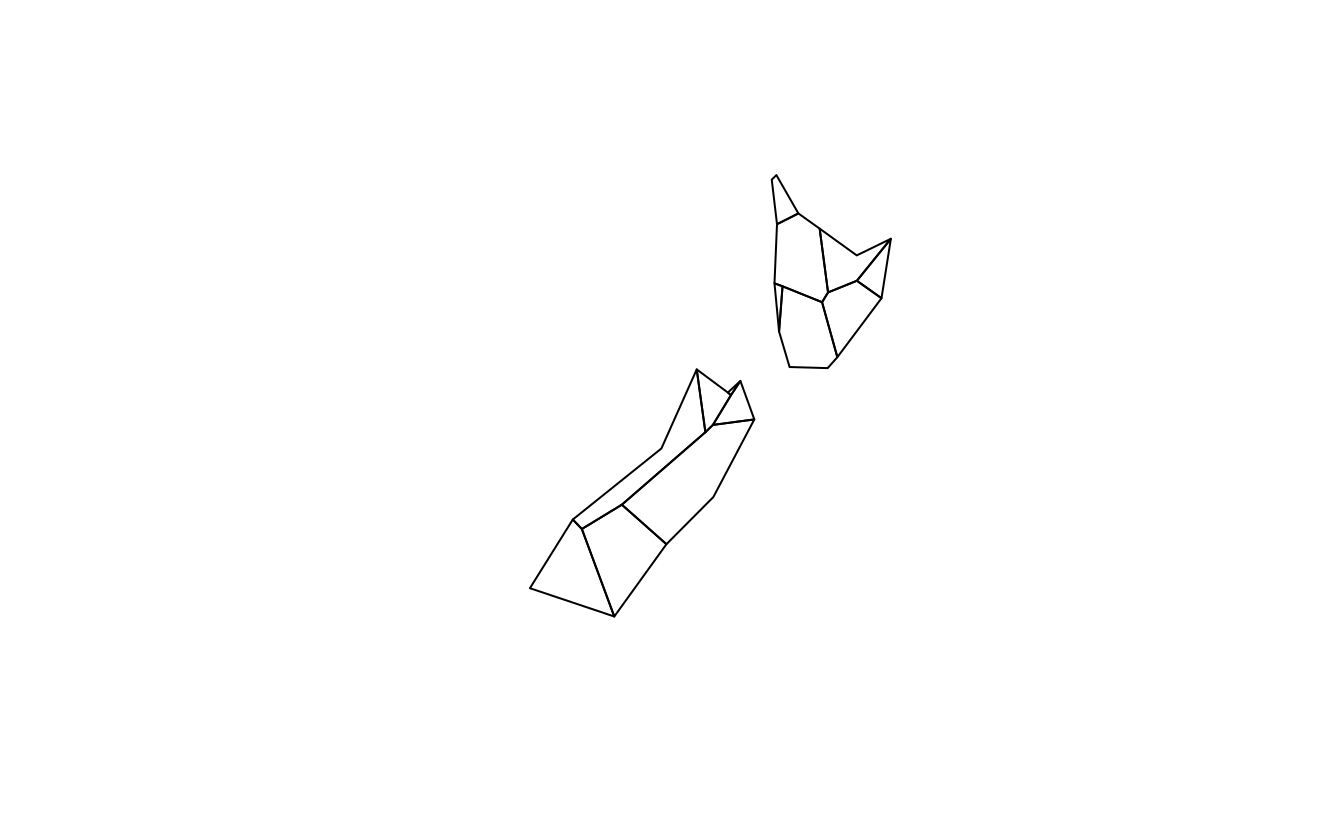
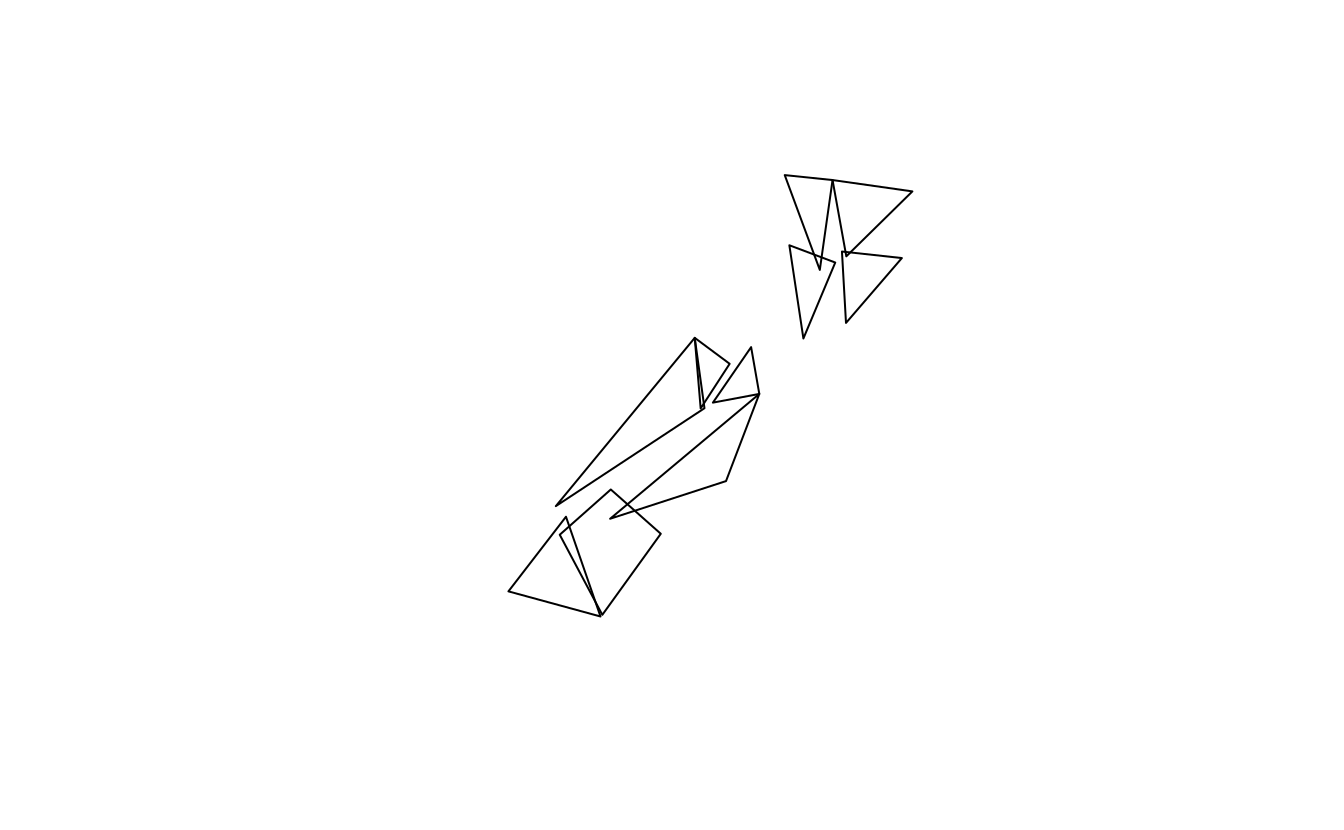
plot(rmapshaper::ms_simplify(st_geometry(nz), keep = 0.5))
plot(rmapshaper::ms_simplify(st_geometry(nz), keep = 0.05))
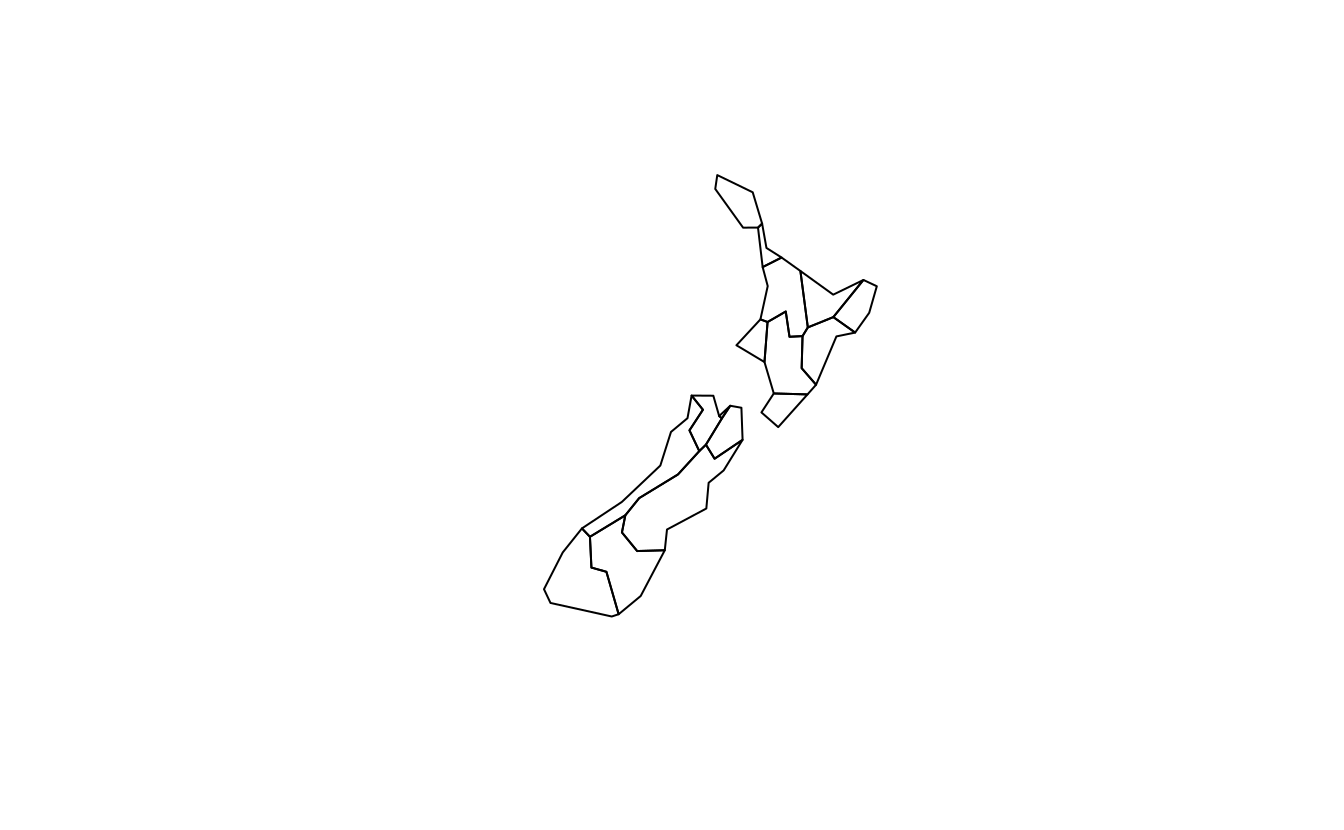
# Starts to breakdown here at 0.5% of the points:
plot(rmapshaper::ms_simplify(st_geometry(nz), keep = 0.005))
# At this point no further simplification changes the result
plot(rmapshaper::ms_simplify(st_geometry(nz), keep = 0.0005))
plot(rmapshaper::ms_simplify(st_geometry(nz), keep = 0.00005))
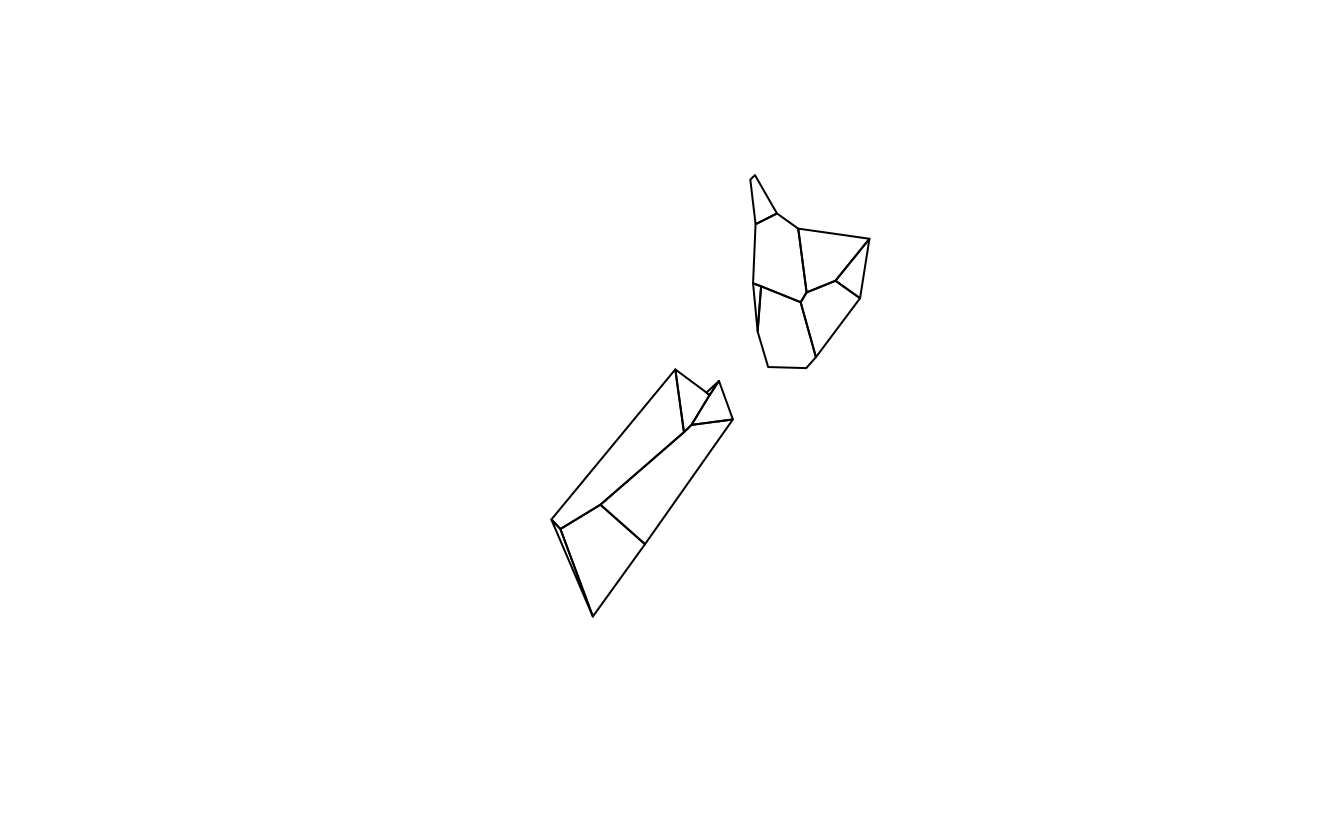
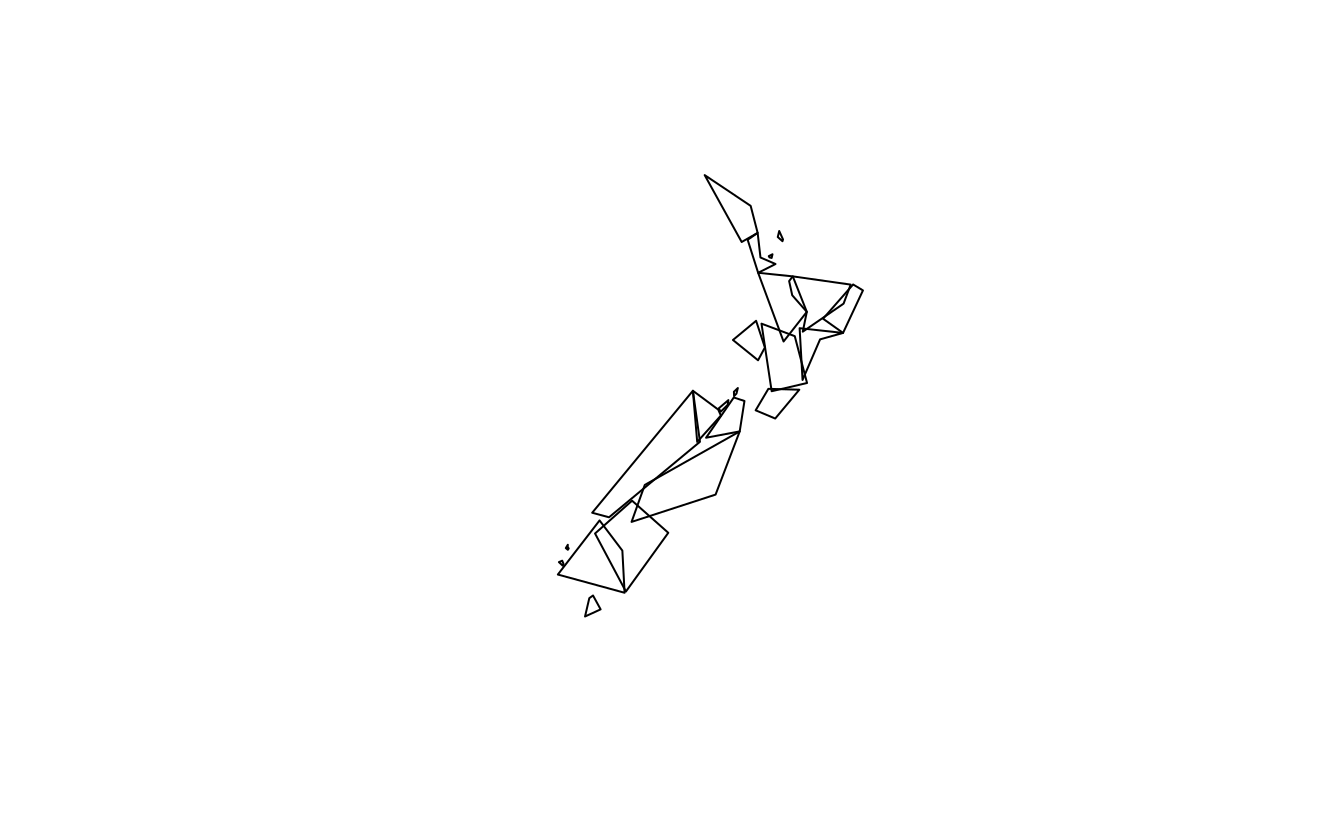
plot(st_simplify(st_geometry(nz), dTolerance = 100))
plot(st_simplify(st_geometry(nz), dTolerance = 1000))
# Starts to breakdown at 10 km:
plot(st_simplify(st_geometry(nz), dTolerance = 10000))
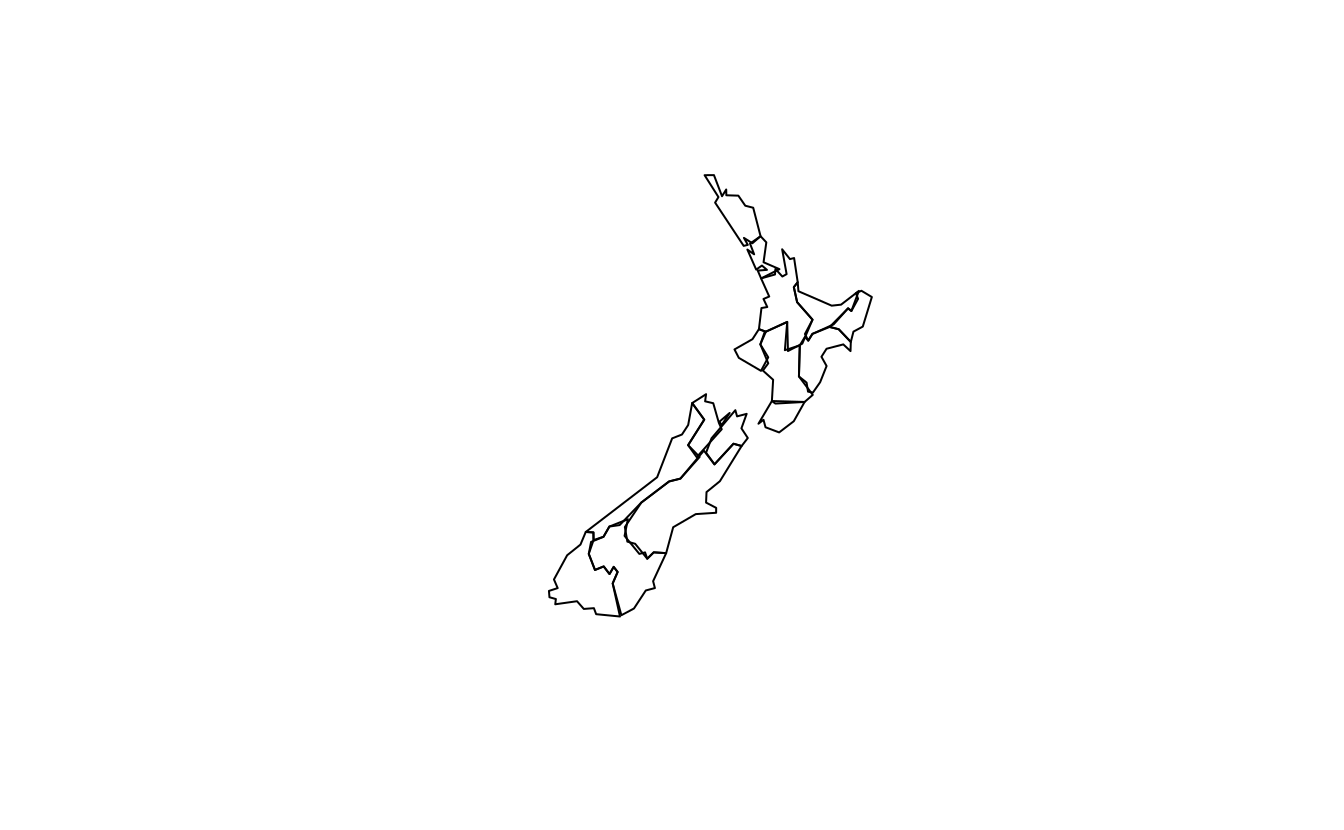
plot(st_simplify(st_geometry(nz), dTolerance = 100000))
plot(st_simplify(st_geometry(nz), dTolerance = 100000, preserveTopology = TRUE))
# Problem: st_simplify returns POLYGON and MULTIPOLYGON results, affecting plotting
# Cast into a single geometry type to resolve this
nz_simple_poly = st_simplify(st_geometry(nz), dTolerance = 10000) |>
st_sfc() |>
st_cast("POLYGON")
#> Warning in st_cast.MULTIPOLYGON(X[[i]], ...): polygon from first part only
#> Warning in st_cast.MULTIPOLYGON(X[[i]], ...): polygon from first part only
nz_simple_multipoly = st_simplify(st_geometry(nz), dTolerance = 10000) |>
st_sfc() |>
st_cast("MULTIPOLYGON")
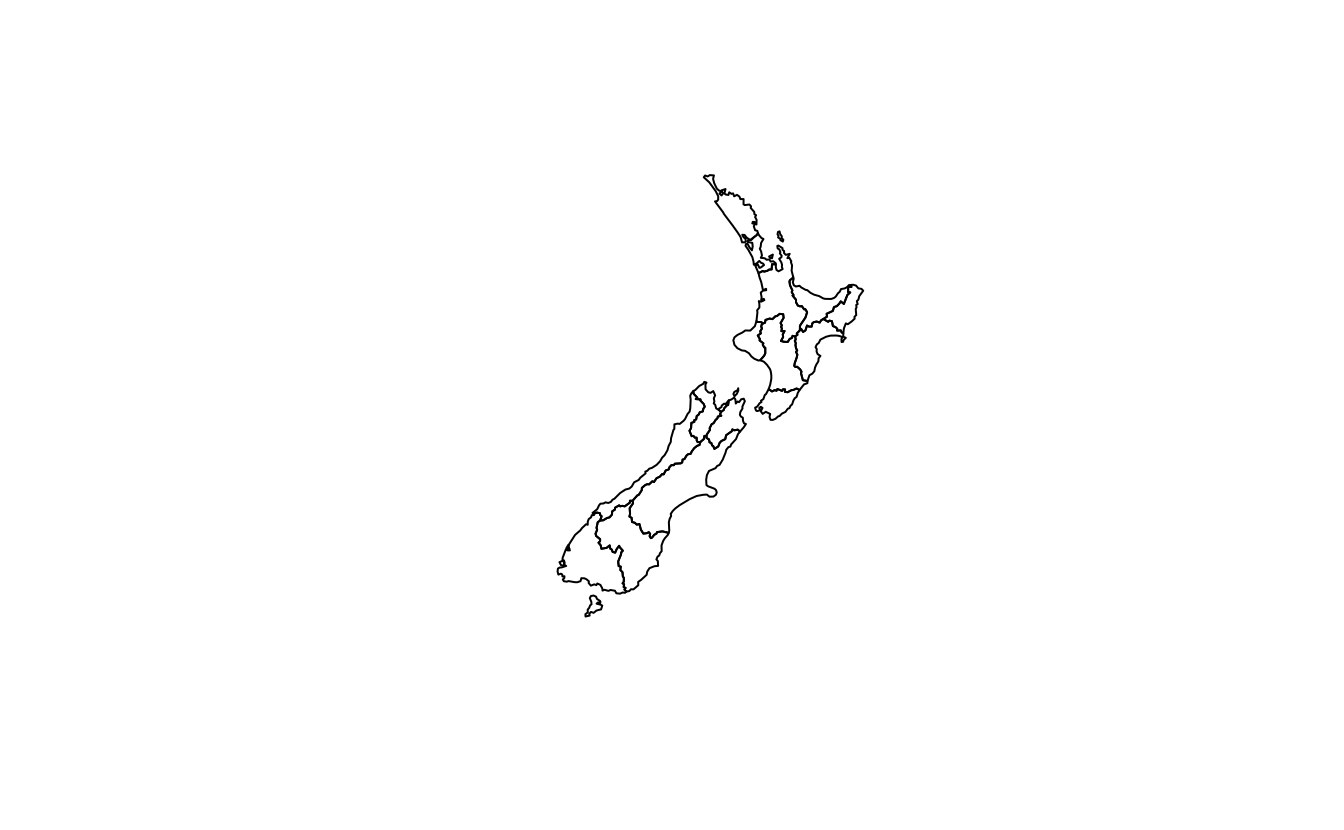
plot(nz_simple_poly)
length(nz_simple_poly)
#> [1] 16
nrow(nz)
#> [1] 16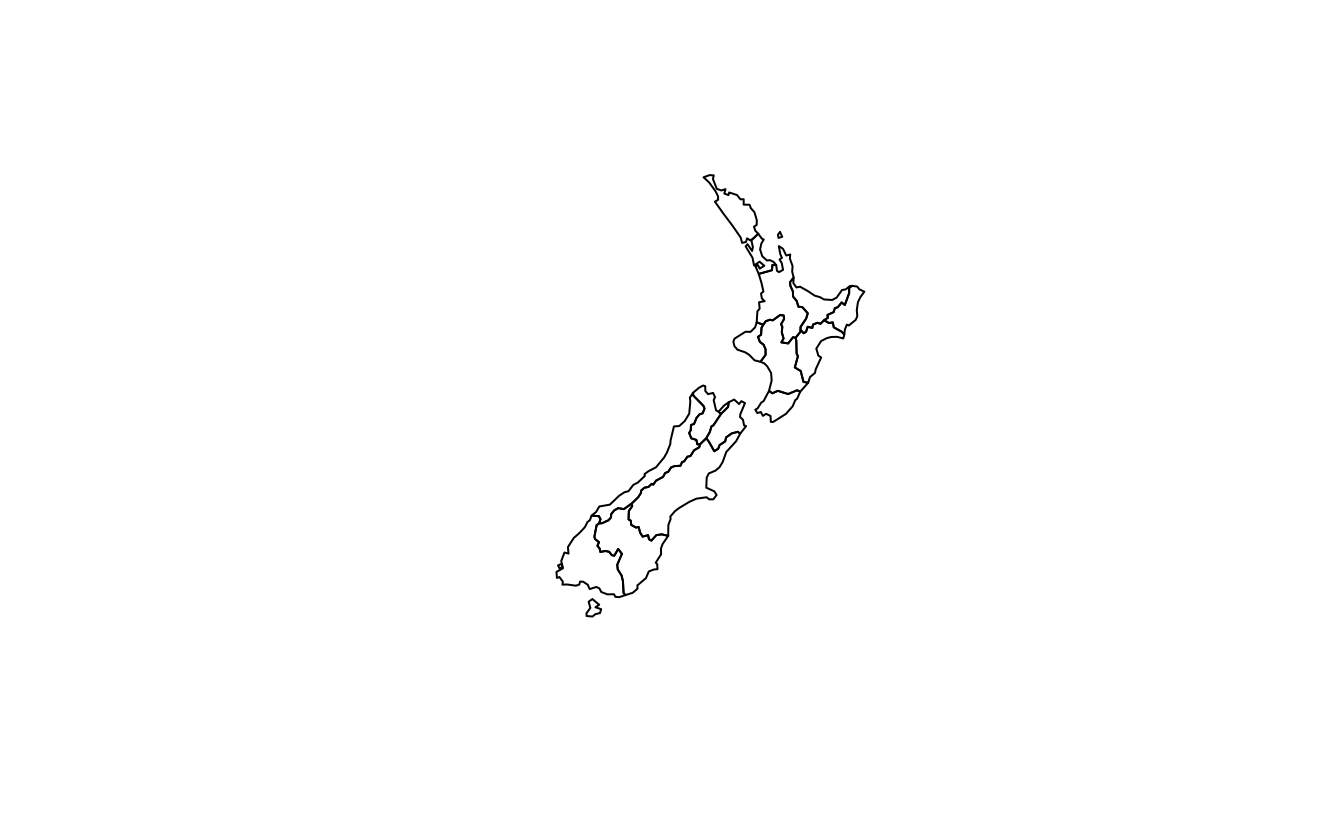

E2. In the first exercise in Chapter Spatial Data Operations it was established that Canterbury region had 70 of the 101 highest points in New Zealand.
Using st_buffer(), how many points in nz_height are within 100 km of Canterbury?
canterbury = nz[nz$Name == "Canterbury", ]
cant_buff = st_buffer(canterbury, 100000)
nz_height_near_cant = nz_height[cant_buff, ]
nrow(nz_height_near_cant) # 75 - 5 more
#> [1] 95E3. Find the geographic centroid of New Zealand. How far is it from the geographic centroid of Canterbury?
cant_cent = st_centroid(canterbury)
#> Warning: st_centroid assumes attributes are constant over geometries
nz_centre = st_centroid(st_union(nz))
st_distance(cant_cent, nz_centre) # 234 km
#> Units: [m]
#> [,1]
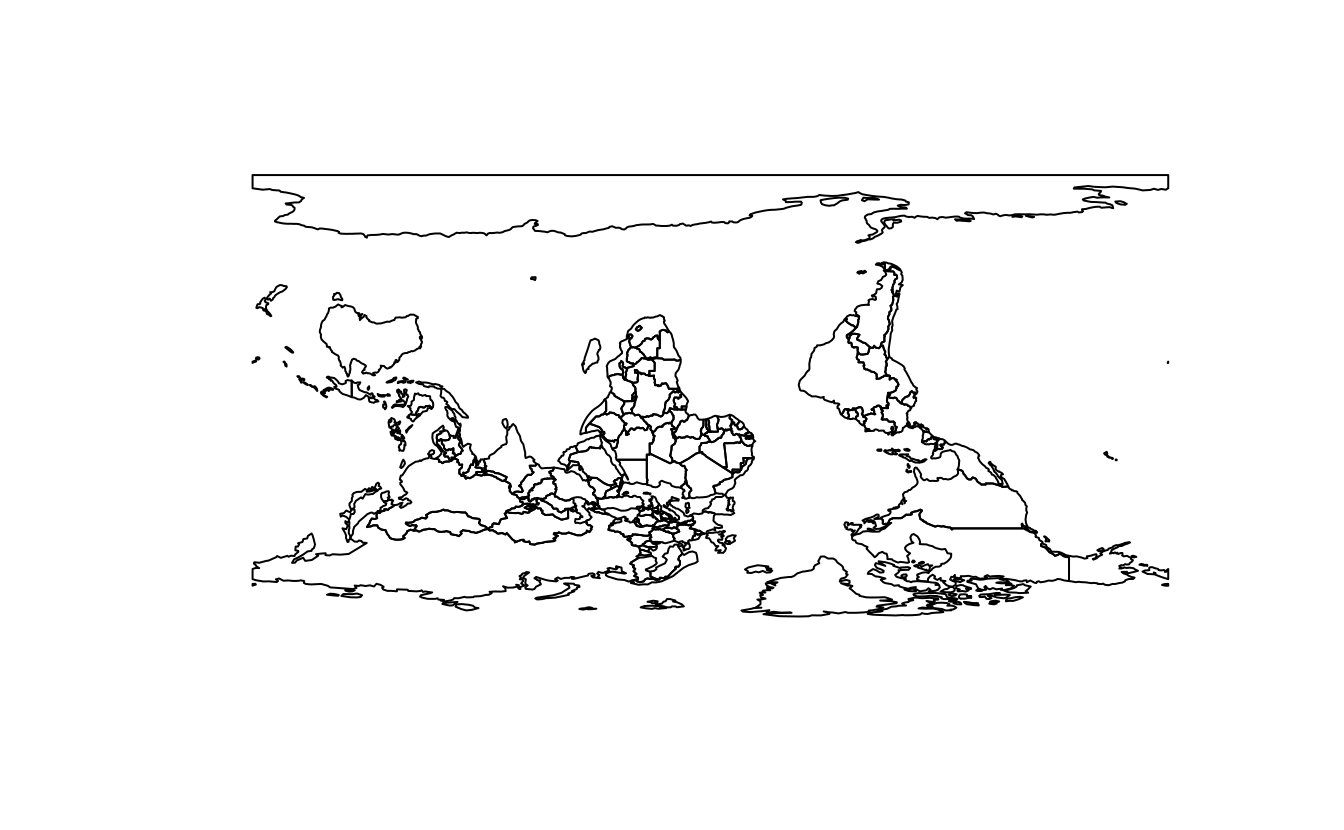
#> [1,] 234193E4. Most world maps have a north-up orientation.
A world map with a south-up orientation could be created by a reflection (one of the affine transformations not mentioned in this chapter) of the world object’s geometry.
Write code to do so.
Hint: you can to use the rotation() function from this chapter for this transformation.
Bonus: create an upside-down map of your country.
rotation = function(a){
r = a * pi / 180 #degrees to radians
matrix(c(cos(r), sin(r), -sin(r), cos(r)), nrow = 2, ncol = 2)
}
world_sfc = st_geometry(world)
world_sfc_mirror = world_sfc * rotation(180)
plot(world_sfc)
plot(world_sfc_mirror)
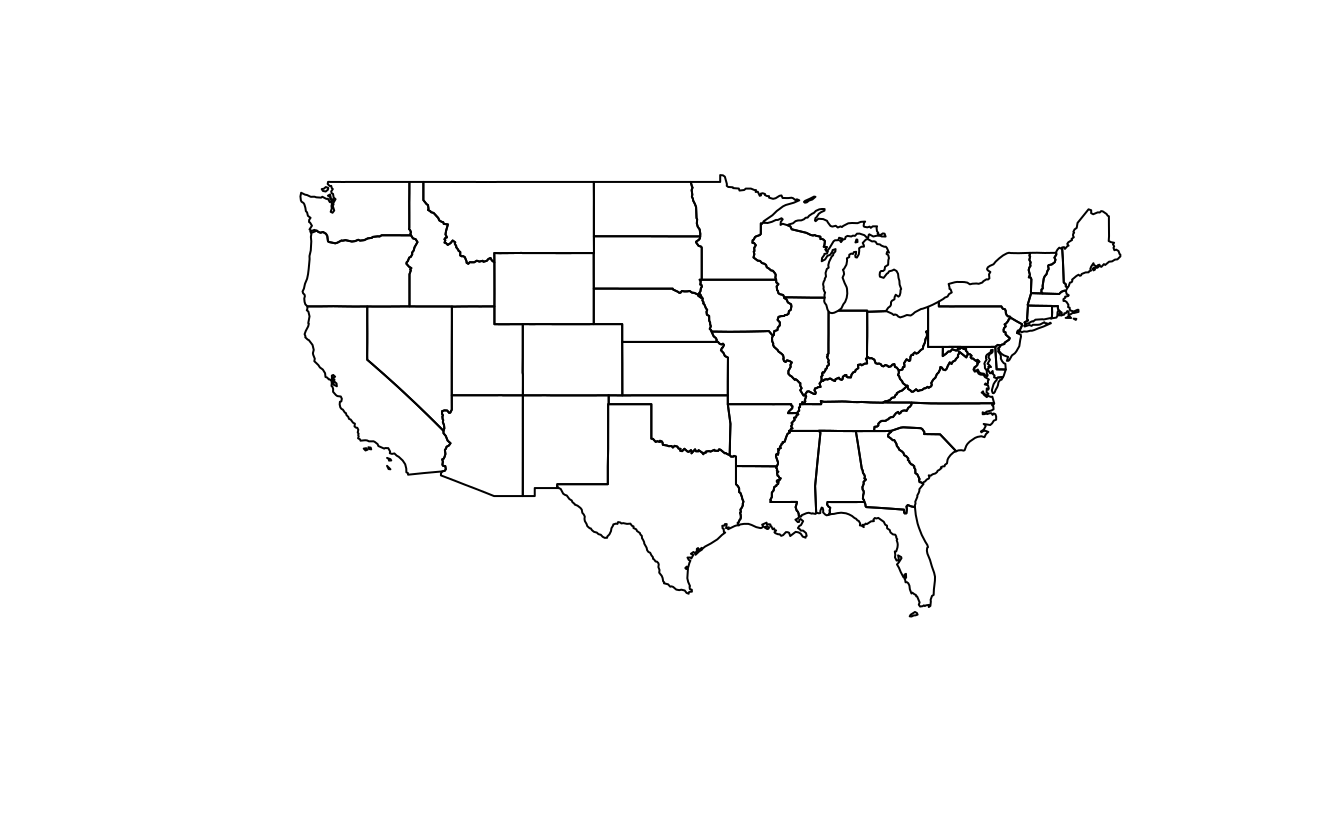
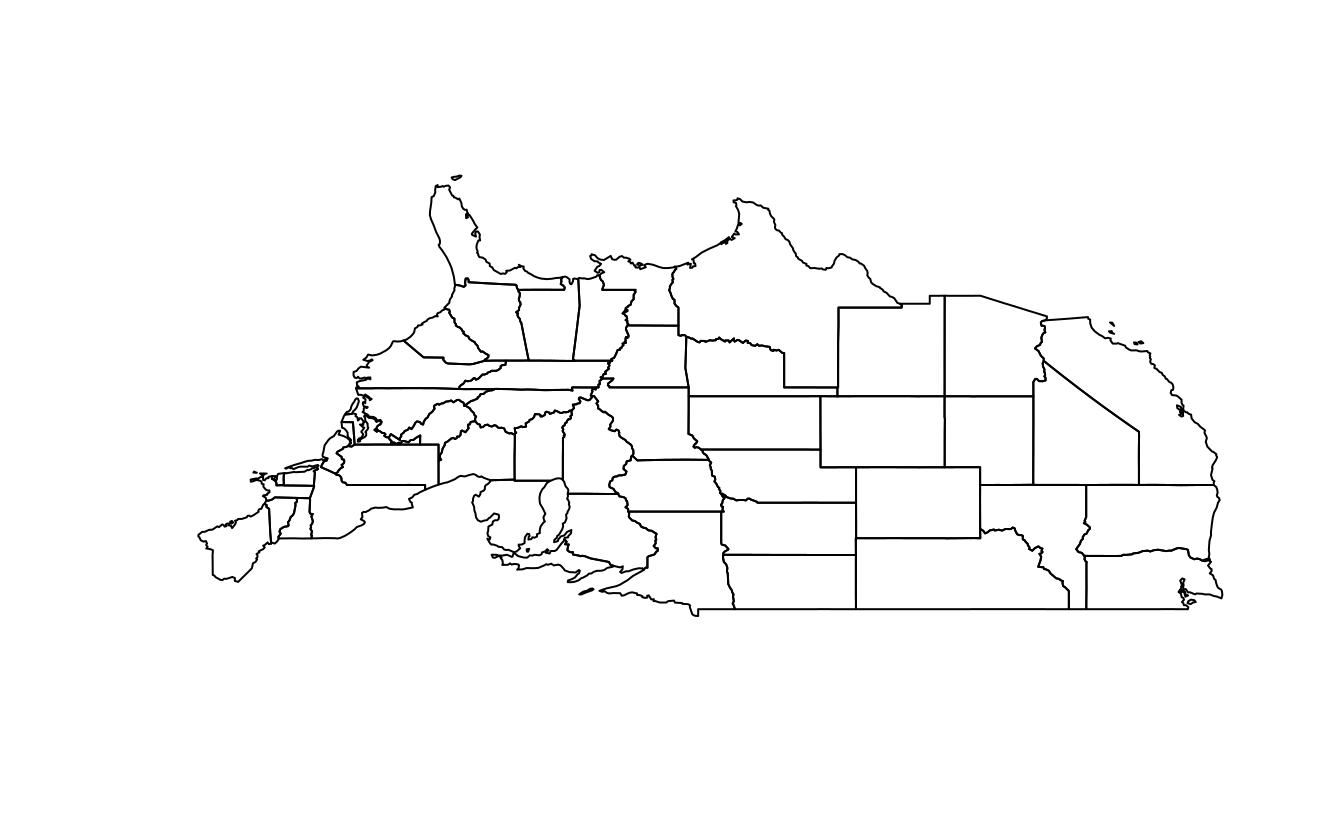
us_states_sfc = st_geometry(us_states)
us_states_sfc_mirror = us_states_sfc * rotation(180)
plot(us_states_sfc)
plot(us_states_sfc_mirror)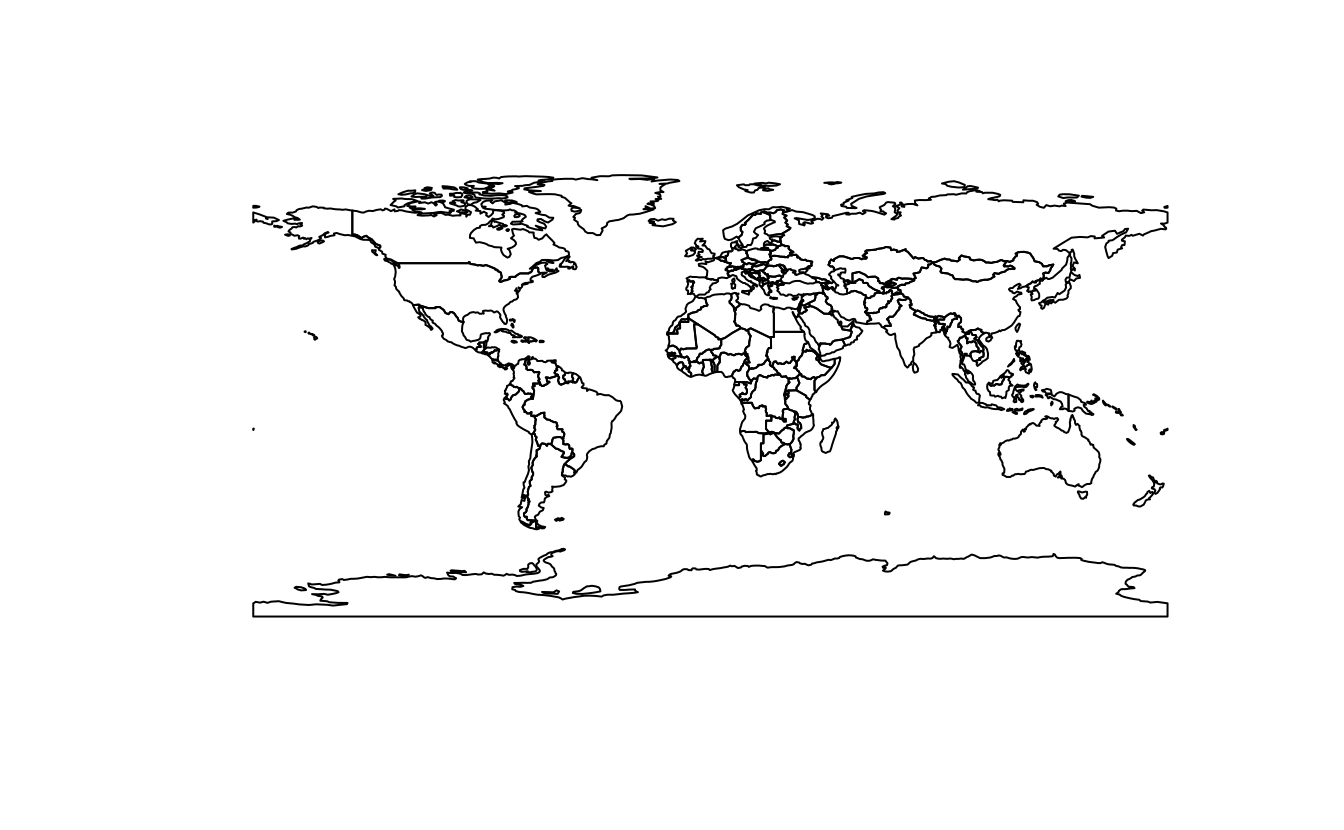
E5. Run the code in Section 5.2.6. With reference to the objects created in that section, subset the point in p that is contained within x and y.
- Using base subsetting operators.
- Using an intermediary object created with
st_intersection().
p_in_y = p[y]
p_in_xy = p_in_y[x]
x_and_y = st_intersection(x, y)
p[x_and_y]
#> Geometry set for 1 feature
#> Geometry type: POINT
#> Dimension: XY
#> Bounding box: xmin: 0.305 ymin: 1.43 xmax: 0.305 ymax: 1.43
#> CRS: NA
#> POINT (0.305 1.43)E6. Calculate the length of the boundary lines of US states in meters.
Which state has the longest border and which has the shortest?
Hint: The st_length function computes the length of a LINESTRING or MULTILINESTRING geometry.
us_states9311 = st_transform(us_states, "EPSG:9311")
us_states_bor = st_cast(us_states9311, "MULTILINESTRING")
us_states_bor$borders = st_length(us_states_bor)
arrange(us_states_bor, borders)
#> Simple feature collection with 49 features and 7 fields
#> Geometry type: MULTILINESTRING
#> Dimension: XY
#> Bounding box: xmin: -2040000 ymin: -2110000 xmax: 2520000 ymax: 731000
#> Projected CRS: NAD27 / US National Atlas Equal Area
#> First 10 features:
#> GEOID NAME REGION AREA total_pop_10 total_pop_15
#> 1 11 District of Columbia South 178 [km^2] 584400 647484
#> 2 44 Rhode Island Norteast 2743 [km^2] 1056389 1053661
#> 3 10 Delaware South 5182 [km^2] 881278 926454
#> 4 09 Connecticut Norteast 12977 [km^2] 3545837 3593222
#> 5 34 New Jersey Norteast 20274 [km^2] 8721577 8904413
#> 6 50 Vermont Norteast 24866 [km^2] 624258 626604
#> 7 33 New Hampshire Norteast 24026 [km^2] 1313939 1324201
#> 8 25 Massachusetts Norteast 20911 [km^2] 6477096 6705586
#> 9 45 South Carolina South 80904 [km^2] 4511428 4777576
#> 10 18 Indiana Midwest 93648 [km^2] 6417398 6568645
#> borders geometry
#> 1 60330 [m] MULTILINESTRING ((1955479 -...
#> 2 304697 [m] MULTILINESTRING ((2338362 4...
#> 3 407939 [m] MULTILINESTRING ((2041302 -...
#> 4 514571 [m] MULTILINESTRING ((2148010 2...
#> 5 747090 [m] MULTILINESTRING ((2062773 -...
#> 6 778660 [m] MULTILINESTRING ((2054045 3...
#> 7 782892 [m] MULTILINESTRING ((2188613 3...
#> 8 1018656 [m] MULTILINESTRING ((2422968 3...
#> 9 1275538 [m] MULTILINESTRING ((1534988 -...
#> 10 1436255 [m] MULTILINESTRING ((1033797 -...
arrange(us_states_bor, -borders)
#> Simple feature collection with 49 features and 7 fields
#> Geometry type: MULTILINESTRING
#> Dimension: XY
#> Bounding box: xmin: -2040000 ymin: -2110000 xmax: 2520000 ymax: 731000
#> Projected CRS: NAD27 / US National Atlas Equal Area
#> First 10 features:
#> GEOID NAME REGION AREA total_pop_10 total_pop_15 borders
#> 1 48 Texas South 687714 [km^2] 24311891 26538614 4959186 [m]
#> 2 06 California West 409747 [km^2] 36637290 38421464 3810350 [m]
#> 3 26 Michigan Midwest 151119 [km^2] 9952687 9900571 3579183 [m]
#> 4 12 Florida South 151052 [km^2] 18511620 19645772 2949048 [m]
#> 5 30 Montana West 380829 [km^2] 973739 1014699 2826586 [m]
#> 6 16 Idaho West 216513 [km^2] 1526797 1616547 2570606 [m]
#> 7 27 Minnesota Midwest 218566 [km^2] 5241914 5419171 2567386 [m]
#> 8 51 Virginia South 105405 [km^2] 7841754 8256630 2407299 [m]
#> 9 35 New Mexico West 314886 [km^2] 2013122 2084117 2378172 [m]
#> 10 53 Washington West 175436 [km^2] 6561297 6985464 2344358 [m]
#> geometry
#> 1 MULTILINESTRING ((-269579 -...
#> 2 MULTILINESTRING ((-1720565 ...
#> 3 MULTILINESTRING ((1113866 1...
#> 4 MULTILINESTRING ((1855611 -...
#> 5 MULTILINESTRING ((-1165102 ...
#> 6 MULTILINESTRING ((-1298509 ...
#> 7 MULTILINESTRING ((202873 44...
#> 8 MULTILINESTRING ((2104821 -...
#> 9 MULTILINESTRING ((-805019 -...
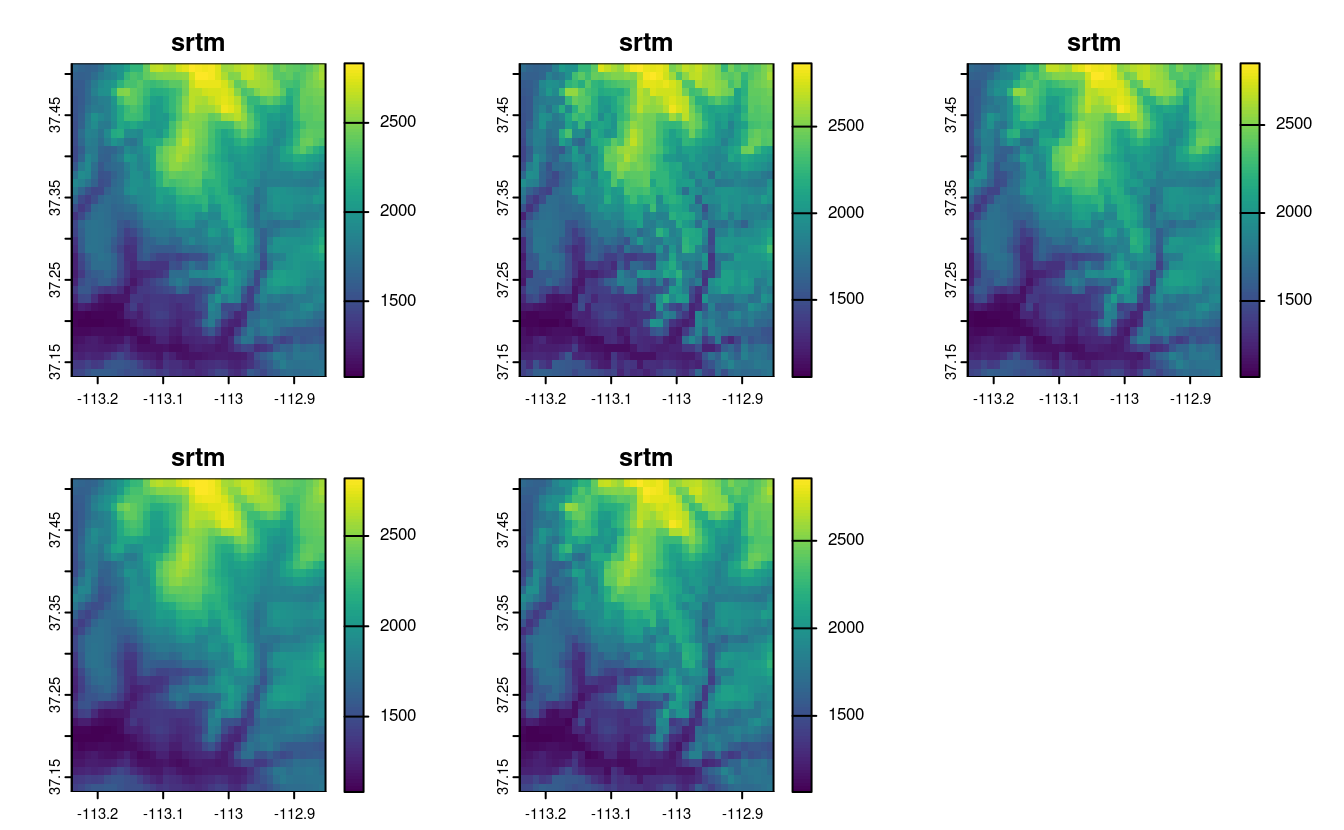
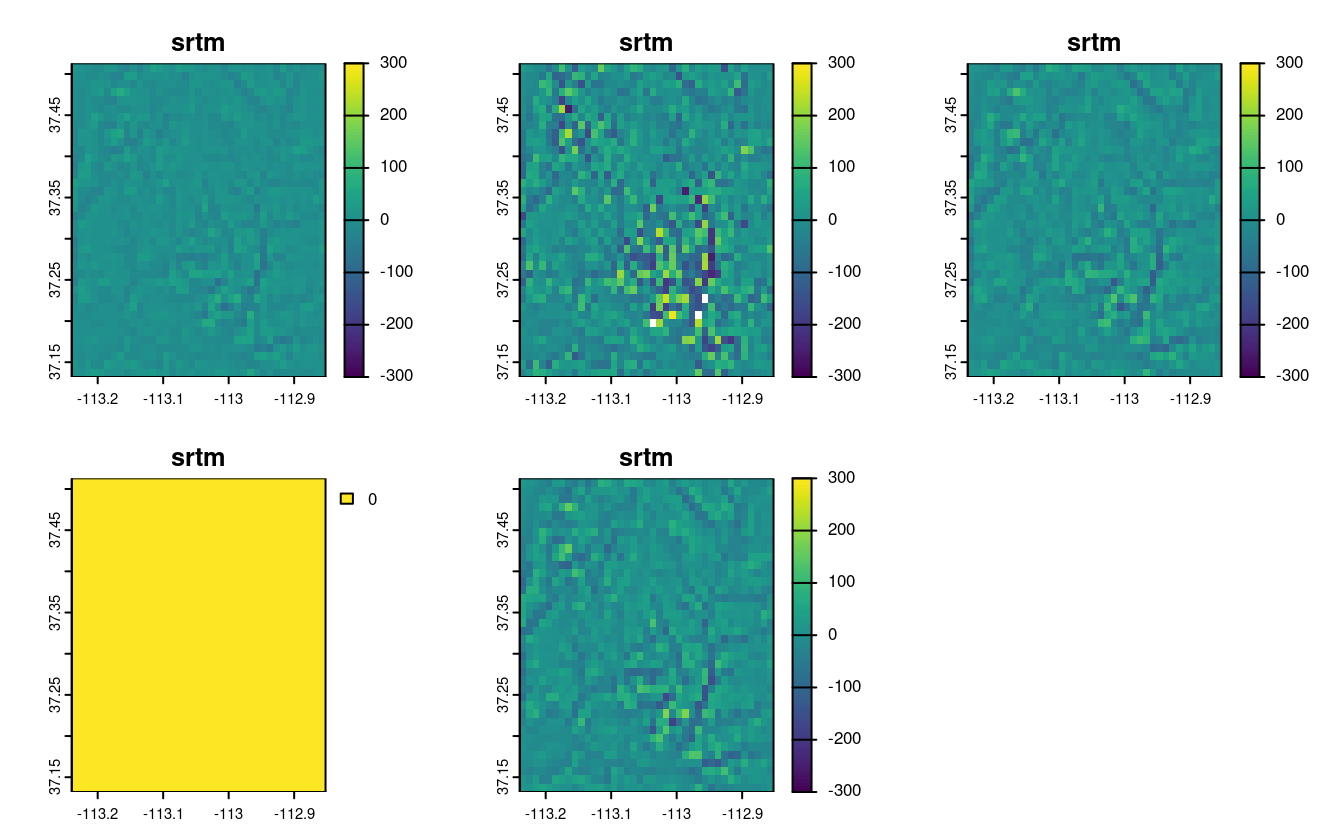
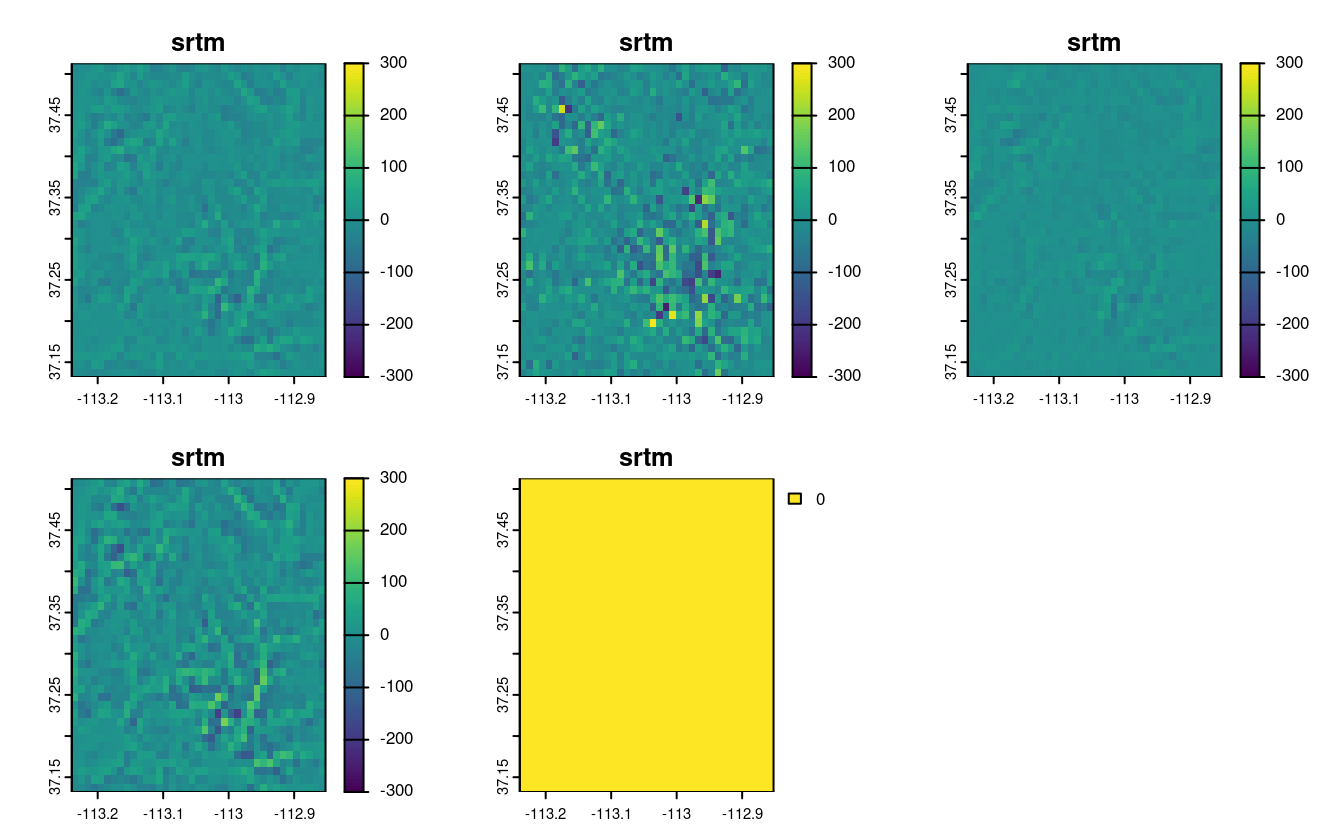
#> 10 MULTILINESTRING ((-1663690 ...E7. Read the srtm.tif file into R (srtm = rast(system.file("raster/srtm.tif", package = "spDataLarge"))).
This raster has a resolution of 0.00083 * 0.00083 degrees.
Change its resolution to 0.01 * 0.01 degrees using all of the methods available in the terra package.
Visualize the results.
Can you notice any differences between the results of these resampling methods?
srtm = rast(system.file("raster/srtm.tif", package = "spDataLarge"))
rast_template = rast(ext(srtm), res = 0.01)
srtm_resampl1 = resample(srtm, y = rast_template, method = "bilinear")
srtm_resampl2 = resample(srtm, y = rast_template, method = "near")
srtm_resampl3 = resample(srtm, y = rast_template, method = "cubic")
srtm_resampl4 = resample(srtm, y = rast_template, method = "cubicspline")
srtm_resampl5 = resample(srtm, y = rast_template, method = "lanczos")
srtm_resampl_all = c(srtm_resampl1, srtm_resampl2, srtm_resampl3,
srtm_resampl4, srtm_resampl5)
plot(srtm_resampl_all)
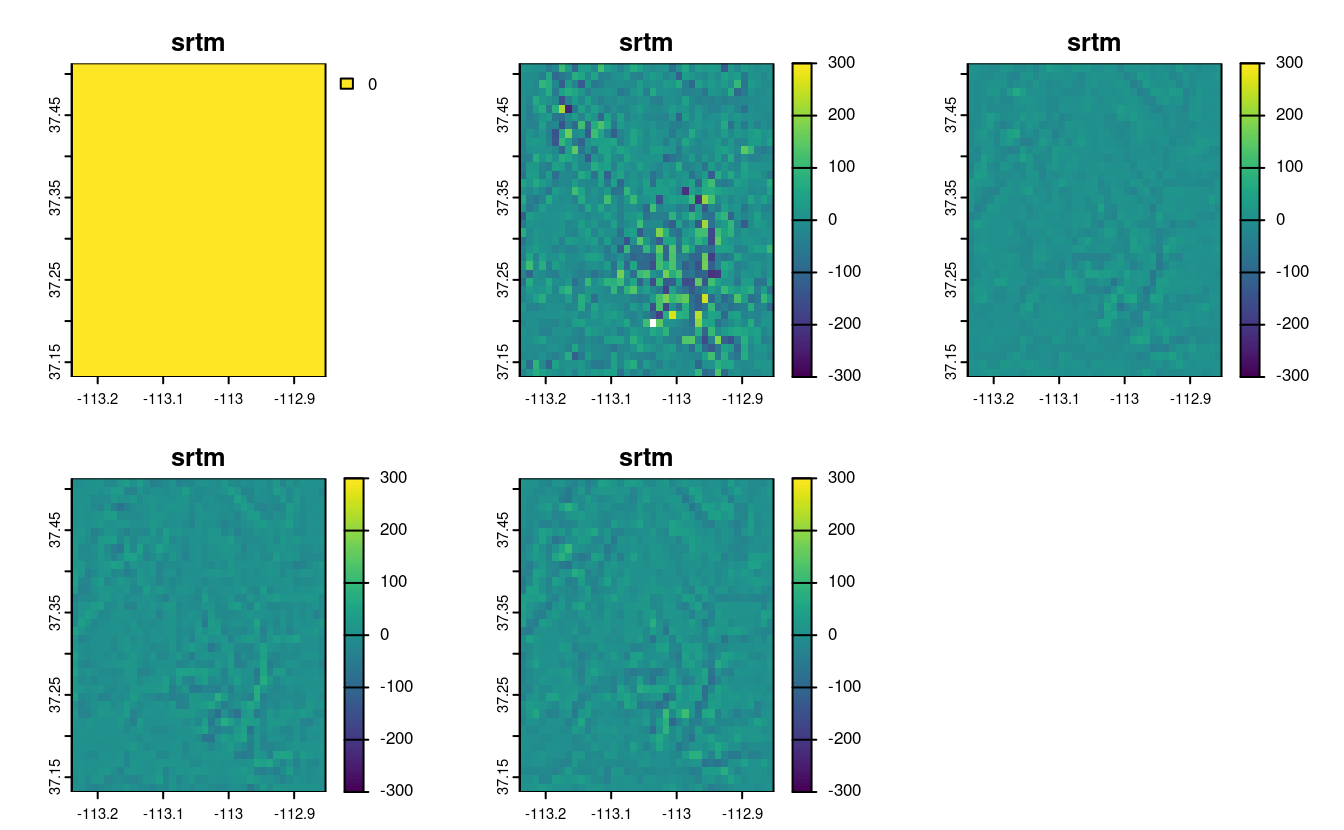
# differences
plot(srtm_resampl_all - srtm_resampl1, range = c(-300, 300))
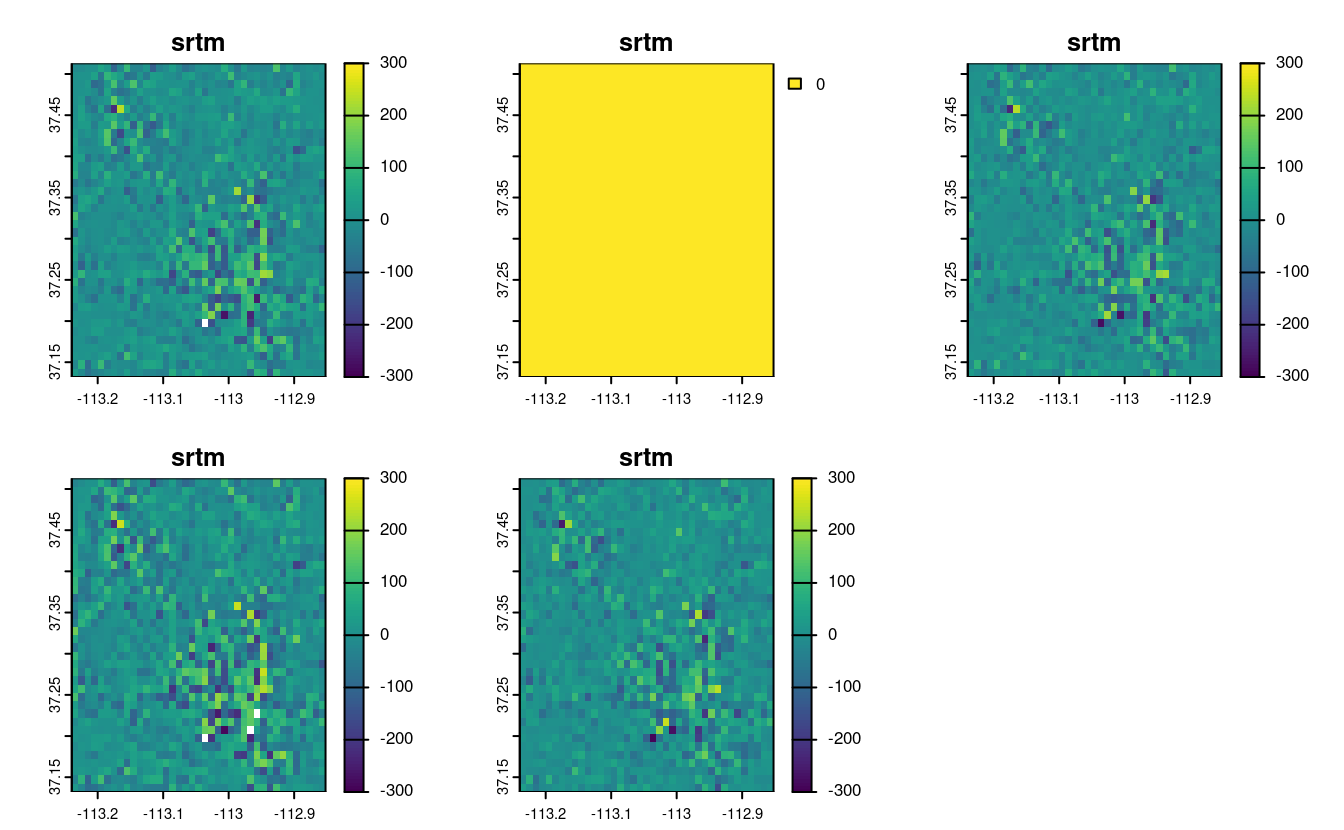
plot(srtm_resampl_all - srtm_resampl2, range = c(-300, 300))
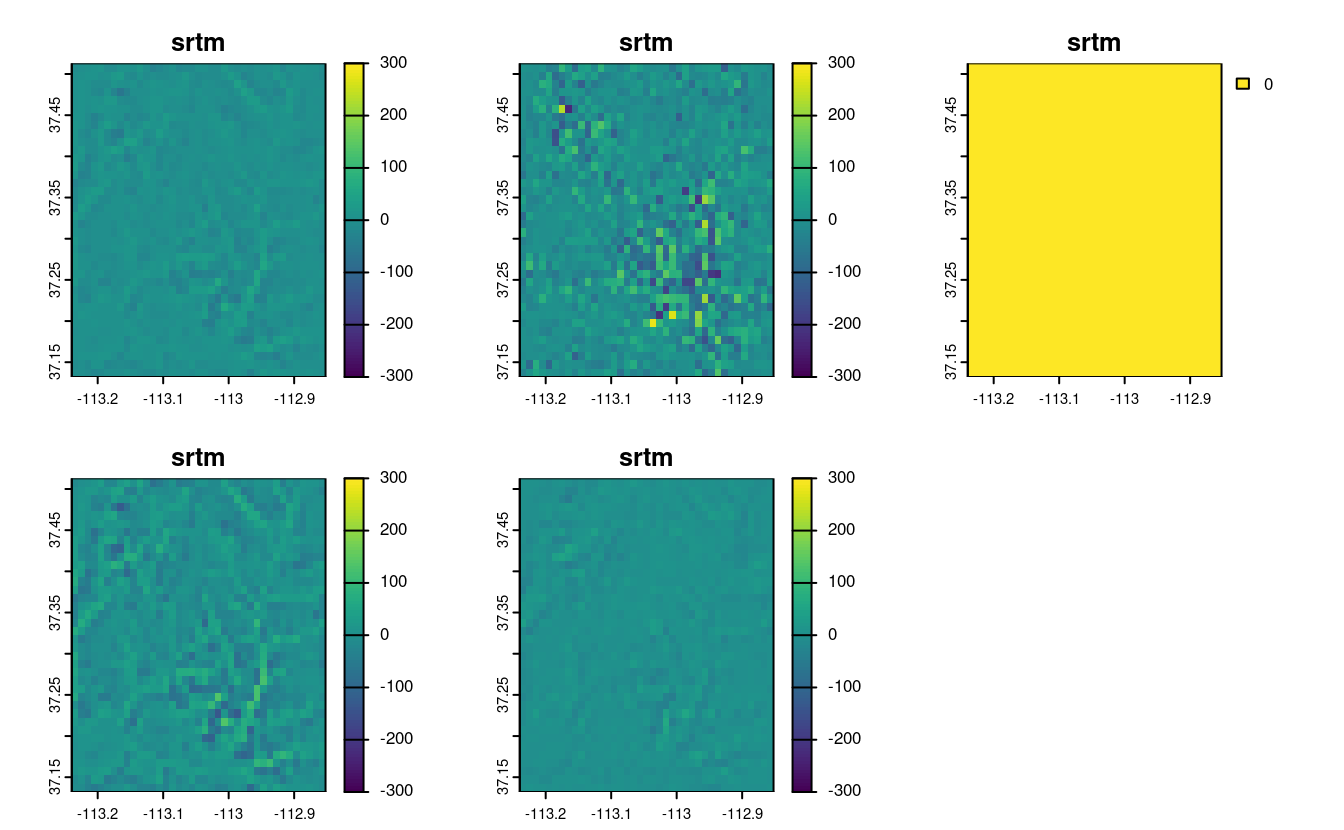
plot(srtm_resampl_all - srtm_resampl3, range = c(-300, 300))
plot(srtm_resampl_all - srtm_resampl4, range = c(-300, 300))
plot(srtm_resampl_all - srtm_resampl5, range = c(-300, 300))